Exploring GPT Models
Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) represent one of the most significant advancements in natural language processing (NLP). By training on massive datasets, these models generate coherent, context-aware text, powering a wide range of applications from chatbots to creative writing assistants. In this in-depth report, we cover technical foundations, real-world use cases, ethical considerations, performance benchmarks, and the future trajectory of GPT technology.
1. Technical Foundations of GPT
At their core, GPT models leverage the Transformer architecture, introduced in 2017, which uses self-attention mechanisms to model relationships between all tokens in a sequence. Each generation—from GPT-1’s 117 million parameters to GPT-4’s multi-hundred-billion scale— has improved understanding of nuance, context, and multilingual capabilities.
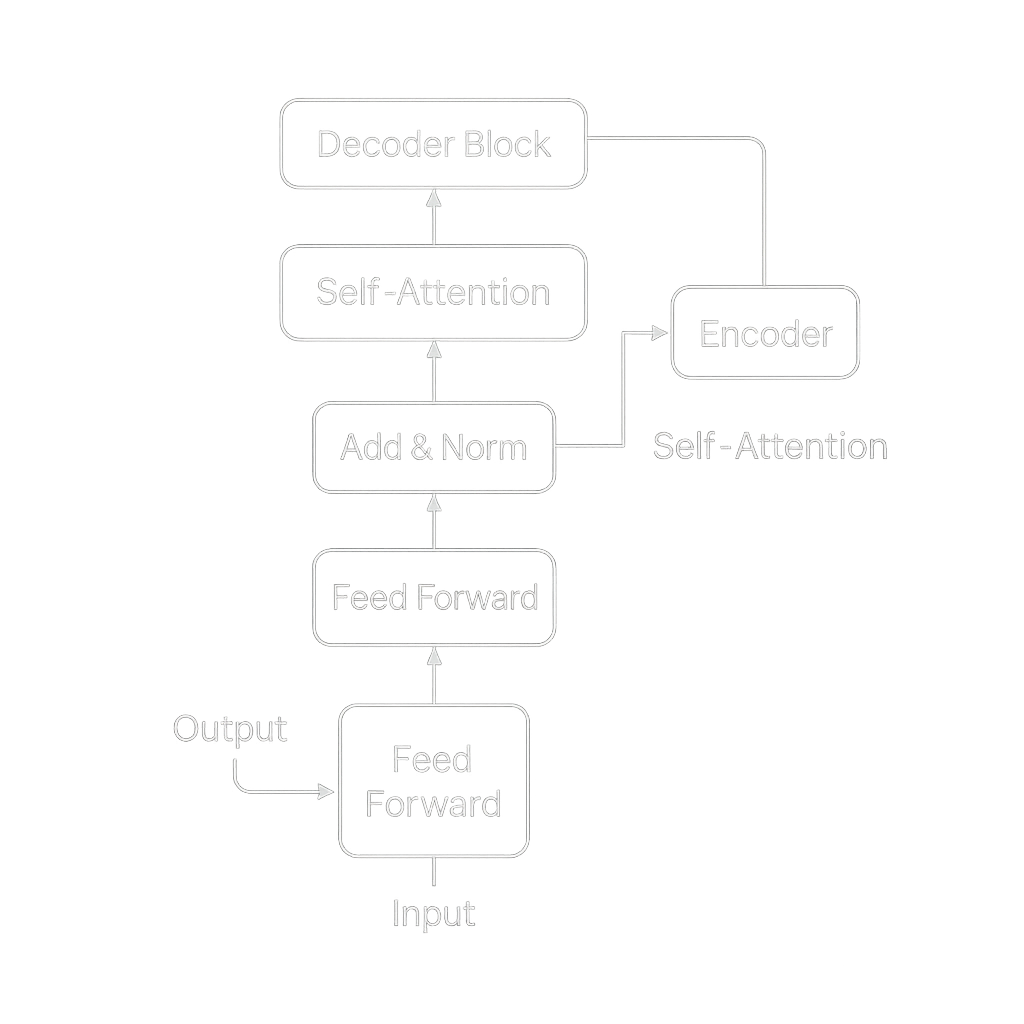
2. Chatbots and Conversational AI
Modern customer-support and virtual-assistant platforms embed GPT for natural interactions. These bots can handle multifaceted queries, personalize recommendations, and escalate to human agents when sentiment analysis detects frustration.
3. Transforming Healthcare Documentation
In clinical environments, GPT automates the drafting of patient notes, summarizing histories, and generating initial diagnostic suggestions. This reduces administrative burden and allows clinicians to focus on direct patient care.
4. Creativity and Content Generation
From novel drafting to marketing copy and screenplay brainstorming, GPT accelerates the creative process. Writers use it to overcome blocks, explore alternative plotlines, and generate multilingual drafts—all under human editorial control.
5. Fine-Tuning and Domain Adaptation
Beyond out-of-the-box performance, GPT can be fine-tuned on domain-specific corpora— legal contracts, financial reports, or scientific papers—enhancing accuracy for specialized tasks like contract review or anomaly detection.
6. Performance Benchmarks
Benchmark metrics such as GLUE, SuperGLUE, and SQuAD illustrate GPT’s rapid progress. Below is a schematic comparison of average scores across major model releases.
7. Ethical, Legal, and Regulatory Challenges
The power of GPT raises questions around privacy, misinformation, and intellectual property. Emerging AI regulations in Europe (AI Act) and the US FTC guidelines push for transparency, bias audits, and user consent disclosures.

8. Future Directions and Resources
Researchers are exploring model distillation for on-device inference, multimodal extensions, and more efficient architectures. To get started:
- OpenAI API & SDKs – official docs and quickstart guides
- Hugging Face Transformers – community‐driven models and demos
- Academic papers – attend NLP conferences for the latest breakthroughs
9. Conclusion
GPT models continue to reshape how organizations and individuals interact with language. With technical enhancements, robust governance, and accessible tooling, we stand on the brink of an AI-driven era where language understanding becomes ubiquitous.






